Clinical Pharmacy and Teaching
Overview
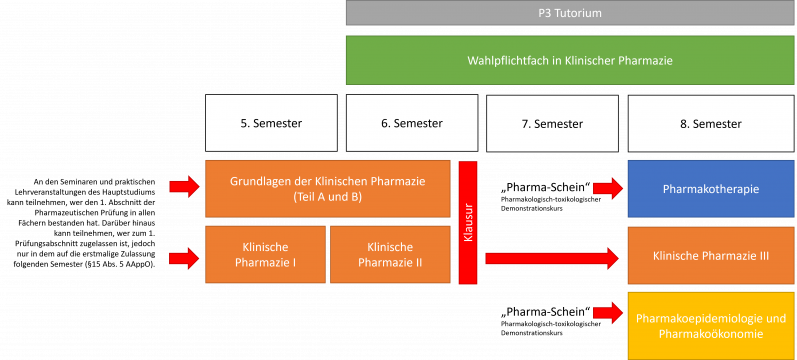
Grundlagen der Klinischen Pharmazie (Basics of Clinical Pharmacy) - Seminar
Clinical drug development and marketing authorisation
Adherence
Drug related problems
Medication review
Klinische Pharmazie I (Clinical Pharmacy I) - Seminar
Communication Seminar
Basic principles of patient-pharmacist interactions and communication theory are the focus of this seminar.
Drug Information and Literature Research
Clinical Studies
Evidence based medicine
Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) is the systematic approach to clinical practice that integrates the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. EBM emphasizes critical appraisal of evidence, applying findings to individual patients, and improving healthcare outcomes. It uses tools like systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and guidelines to inform decision-making and ensure the most effective, safe, and patient-centered care.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the Core Principles: Define evidence-based medicine and its importance in improving healthcare quality.
- Critically Appraise Evidence: Develop skills to assess the validity, reliability, and applicability of research studies.
- Integrate Evidence with Practice: Learn to apply research findings in clinical decision-making tailored to patient needs and preferences.
- Use EBM Tools: Understand and use resources like clinical guidelines, systematic reviews, and databases (e.g., Cochrane Library).
- Promote Shared Decision-Making: Balance evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values in collaborative healthcare planning.
- Enhance Continuous Learning: Foster a commitment to ongoing learning and keeping current with the latest research and practices.
Hands on Seminar: pharmaceutical Services (pDL: Inhalativa und Blutdruckmessung)
Klinische Pharmazie II (Clinical Pharmacy II) - Seminar
Evidence based over the counter (OTC) medicines
Evidence-based over-the-counter (OTC) medicines involve the evaluation and use of non-prescription drugs based on high-quality clinical evidence. This approach ensures that OTC treatments are safe, effective, and appropriate for self-care. By integrating research findings with practical guidance, healthcare providers and consumers can make informed decisions about OTC medicine use, minimizing risks and optimizing health outcomes.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand OTC Medicines: Define the role of OTC medicines in healthcare and their accessibility for self-care.
- Appraise Evidence: Learn to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and quality of evidence supporting OTC medications.
- Recognize Appropriate Use: Identify conditions for which evidence supports the use of OTC medicines and recognize their limitations.
- Address Safety Concerns: Understand potential risks, including drug interactions, misuse, and overuse, associated with OTC products.
- Promote Informed Choices: Guide patients in selecting and using OTC medicines based on evidence and individual health needs.
- Support Public Health: Explore the role of evidence-based OTC medicines in reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Drug therapy and organ dysfunction
Drug therapy in liver and kidney dysfunction focuses on adapting pharmacological treatments to account for impaired hepatic and renal function. These conditions significantly affect drug metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetics, necessitating dose adjustments to avoid toxicity and ensure therapeutic efficacy. Understanding these changes is critical for safe and effective medication management in patients with liver or kidney dysfunction.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Pharmacokinetic Changes: Learn how liver and kidney dysfunction impact drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion.
- Adjust Dosing Regimens: Develop strategies for modifying drug dosages and intervals in hepatic and renal impairment.
- Identify High-Risk Medications: Recognize drugs that require caution or are contraindicated in these conditions.
- Monitor for Toxicity: Understand the signs of drug accumulation and toxicity in patients with impaired organ function.
- Incorporate Laboratory Values: Use markers like liver enzymes, creatinine clearance, and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to guide therapy adjustments.
- Optimize Therapeutic Outcomes: Balance efficacy and safety in drug selection and dosing to improve patient outcomes in these complex conditions.
Special Populations: Geriatrics, Pregnant, Pediatrics
Drug therapy in special populations focuses on adapting pharmacological treatments to meet the unique physiological and clinical needs of geriatrics, pregnant women, and pediatric patients. Each group experiences distinct pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes that influence drug efficacy and safety. Tailoring medication regimens for these populations is essential to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing risks.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Population-Specific Differences: Learn how aging, pregnancy, and developmental stages affect drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion.
- Optimize Drug Dosing: Develop strategies to individualize dosages based on physiological changes, such as reduced renal clearance in geriatrics, altered plasma volume in pregnancy, or immature enzyme systems in pediatrics.
- Recognize High-Risk Medications: Identify drugs to avoid or use with caution in these populations due to potential toxicity or adverse effects.
- Address Safety Concerns: Understand how to prevent medication errors, adverse drug reactions, and interactions specific to each group.
- Incorporate Guidelines and Evidence: Apply evidence-based recommendations and regulatory guidelines for drug use in geriatrics, pregnancy, and pediatrics.
- Promote Patient-Centered Care: Balance clinical evidence with individual needs, values, and preferences to ensure safe and effective treatment.
- Mastering these principles ensures healthcare providers can deliver age- and condition-appropriate care, improving health outcomes for vulnerable populations.
Klinische Pharmazie III (Clinical Pharmacy III) - Seminar
Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of how an individual’s genetic makeup influences their response to drugs. By understanding genetic variations that affect drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity, pharmacogenomics enables personalized medicine. This approach optimizes drug selection and dosing, reduces adverse drug reactions, and improves therapeutic outcomes, making it a cornerstone of precision healthcare.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Key Concepts: Define pharmacogenomics and its role in tailoring drug therapy based on genetic differences.
- Identify Genetic Variations: Learn about common genetic polymorphisms affecting drug metabolism (e.g., CYP450 enzymes) and response.
- Optimize Drug Therapy: Use pharmacogenomic data to personalize drug selection and dosing to maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity.
- Evaluate Evidence and Tools: Understand the use of genetic testing, biomarkers, and clinical guidelines in pharmacogenomics.
- Address Ethical Considerations: Explore ethical, legal, and social implications of pharmacogenomic testing, such as privacy and access.
- Integrate into Clinical Practice: Learn strategies for incorporating pharmacogenomic information into routine healthcare and decision-making.
Dose Individualization and Therapy Monitoring
Dose individualization and therapy monitoring involve tailoring drug dosages and monitoring therapeutic responses to meet the specific needs of individual patients. This approach considers factors such as age, weight, organ function, genetic profile, and drug interactions. By optimizing dosing regimens and actively monitoring therapy, healthcare providers enhance treatment efficacy and minimize adverse effects.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the Importance of Individualization: Learn why personalized dosing is critical for maximizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing risks.
- Identify Key Patient Factors: Recognize how factors like age, body weight, renal and hepatic function, and comorbidities affect drug dosing.
- Apply Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Use concepts like half-life, clearance, and drug-receptor interactions to guide dose adjustments.
- Utilize Monitoring Techniques: Understand tools like therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) and biomarkers to assess drug levels and therapeutic responses.
- Adapt to Dynamic Changes: Learn to adjust doses based on ongoing patient changes, such as disease progression or drug interactions.
- Promote Safe and Effective Therapy: Develop strategies to balance efficacy and safety, preventing under- or overdosing.
Clinical Laboratory Data
Clinical laboratory data plays a critical role in guiding drug therapy by providing objective measures of a patient’s health status. These data inform diagnosis, monitor therapeutic efficacy, detect adverse effects, and guide dose adjustments. Proper interpretation of laboratory results ensures evidence-based decision-making and personalized treatment strategies.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Key Laboratory Parameters: Learn about essential lab tests, including blood chemistry, liver and kidney function tests, and hematological profiles, and their relevance to drug therapy.
- Interpret Lab Results: Develop skills to analyze clinical laboratory data to identify abnormalities that may impact drug therapy.
- Monitor Therapy Outcomes: Use laboratory results to assess the effectiveness and safety of ongoing treatment.
- Guide Dose Adjustments: Learn how lab parameters like creatinine clearance, INR, or liver enzymes influence drug dosing and regimen modifications.
- Detect Adverse Drug Effects: Recognize laboratory markers indicative of drug toxicity or adverse reactions, such as elevated liver enzymes or blood dyscrasias.
- Integrate Lab Data in Clinical Decisions: Combine laboratory data with clinical findings to provide evidence-based, individualized care.
Pharmakotherapie (Pharmacotherapy) - Seminar
Cancer Therapy
Cancer therapy encompasses a range of treatment modalities designed to target and eliminate cancer cells while minimizing harm to normal tissues. These approaches include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation, and surgical interventions. Tailoring cancer treatment involves considering tumor type, stage, genetic mutations, and patient-specific factors to maximize efficacy and reduce adverse effects.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Treatment Modalities: Learn about different cancer therapies, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and their mechanisms of action.
- Individualize Therapy: Develop strategies for personalizing cancer treatment based on tumor genetics, biomarkers, and patient factors.
- Recognize Adverse Effects: Identify common toxicities associated with cancer therapies and strategies for their prevention and management.
- Incorporate Pharmacogenomics: Understand the role of genetic testing in predicting drug response and tailoring cancer treatments.
- Evaluate Therapy Outcomes: Learn to monitor treatment efficacy using clinical, radiological, and laboratory parameters.
- Integrate Multimodal Approaches: Understand how to combine various treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes and reduce resistance.
Cardiovascular diseases
Treatment of Diabetes mellitus
Pulmonary diseases
Pharmakoepidemiologie und Pharmakoökonomie (Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics) - Seminar
Pharmacoepidemiology
Pharmacoepidemiology is the study of the use and effects of drugs in large populations. It combines principles of pharmacology and epidemiology to evaluate drug safety, efficacy, and patterns of use. The discipline aims to identify and quantify adverse drug reactions, optimize therapeutic outcomes, and inform regulatory decisions. By analyzing data from clinical trials, registries, and observational studies, pharmacoepidemiology provides insights into real-world drug performance and public health impacts.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Core Concepts: Define and explain the principles of pharmacoepidemiology and its role in public health.
- Evaluate Drug Safety: Identify methods to detect and assess adverse drug reactions and other safety concerns.
- Analyze Data Sources: Understand the types of data used in pharmacoepidemiological research, including their strengths and limitations.
- Apply Epidemiological Methods: Learn to apply study designs (e.g., cohort studies, case-control studies) to evaluate drug use and outcomes.
- Inform Decision-Making: Use evidence from pharmacoepidemiology to support clinical and regulatory decisions.
- Address Ethical Challenges: Explore ethical considerations in conducting pharmacoepidemiological research, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Pharmacoeconomics
Pharmacoeconomics examines the costs and outcomes associated with pharmaceutical products and therapies. It aims to assess the value of drugs by balancing their economic impact against their clinical benefits. By employing methods such as cost-effectiveness, cost-utility, and cost-benefit analyses, pharmacoeconomics supports resource allocation decisions in healthcare. The discipline is essential for evaluating the affordability and sustainability of treatments in diverse healthcare systems.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand Fundamental Concepts: Define pharmacoeconomics and its importance in healthcare decision-making.
- Analyze Economic Evaluations: Differentiate between various economic evaluation methods (e.g., cost-effectiveness, cost-utility).
- Assess Drug Value: Learn to quantify the economic and clinical impact of pharmaceutical interventions.
- Interpret Key Metrics: Understand and apply metrics like quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs).
- Inform Policy and Practice: Use pharmacoeconomic evidence to guide formulary decisions and resource allocation in healthcare systems.
- Address Ethical and Social Issues: Explore challenges related to affordability, equity, and access to medicines.
Wahlpflichtpraktikum in Klinischer Pharmazie (Compulsory elective internship in clinical pharmacy)
P³-Tutorium